Uncategorized
Berberine – a Natural Aid for Supporting Blood Sugar Balance and Metabolism
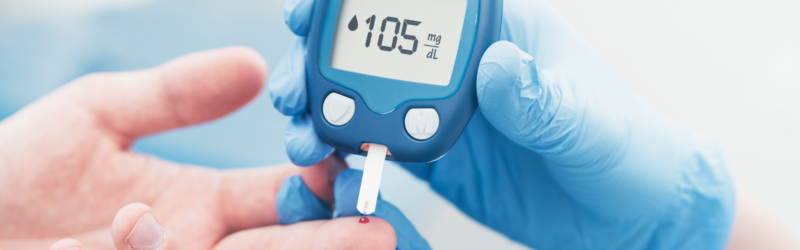
Our daily dietary and lifestyle choices significantly affect how our body processes sugar. If blood sugar levels are consistently high or highly fluctuating, this can eventually lead to insulin resistance, metabolic disorders, and an increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
Berberine is gaining prominence as a natural plant compound that has been used for centuries in traditional medicine, and its positive effect on maintaining blood sugar balance has also been confirmed in modern scientific research.
What is Berberine?
Berberine is a bioactive alkaloid found in various medicinal plants, including common barberry (Berberis vulgaris). It imparts a characteristic rush-yellow hue to these plants and is known for its antibacterial, digestive enzyme-supporting, and metabolism-regulating properties.
Berberine has been used for centuries in Chinese medicine to support digestion, circulation, and blood purification. Today, it is primarily studied as a moderate supporter of blood sugar and lipid metabolism.[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Berberine]
How Does Berberine Work?
1. Activates the AMPK Enzyme Pathway
Berberine activates intracellular AMPK (adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase) – the metabolic “master switch” – which increases energy production and improves cells’ ability to utilize glucose. This process helps the body metabolize sugar more efficiently.
[https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0753332220311768]
2. Slows Down Carbohydrate Absorption
Berberine slows down the breakdown and absorption of carbohydrates in the small intestine, which helps prevent rapid blood sugar spikes after meals.
3. Supports Gut Microbiome
Studies have shown that berberine positively influences the balance of gut bacteria, which in turn is linked to metabolism and immune system function.
[https://pmc .ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC8874997 /]
4. Antioxidant and Anti-inflammatory Effects
Berberine helps reduce oxidative stress and chronic low-grade inflammation, which are associated with metabolic disorders and the aging process.
[https://pmc .ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC8107691 /]
What Do Clinical Studies Show?
Improves Glucose Balance and Insulin Sensitivity: Berberine has proven effective in lowering glucose levels and improving insulin sensitivity in patients with type 2 diabetes. [https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1155/2021/2074610]
Effect Comparable to Metformin: Berberine’s effect has been compared to the diabetes drug metformin in some studies, with results showing comparable moderate efficacy.
[https://pubmed .ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26088325 /]
Supports Lipid Metabolism and Weight Loss: Berberine contributes to fat metabolism and may support weight reduction in conjunction with a balanced diet.
[https://pubmed .ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20370677 /]
How to Use Berberine?
Dosage: Typically, 500 mg is used twice daily.
Best Time: Approximately 20–30 minutes before meals, especially carbohydrate-rich ones.
Duration: Suitable for long-term use, but consultation with a healthcare professional is advisable for chronic conditions.
Safety and Side Effects
Berberine is generally safe when used in recommended doses. Possible temporary side effects may include:
* digestive issues (e.g., gas, nausea);
* drug interactions (e.g., with blood pressure, diabetes, or cholesterol medications);
* not recommended during pregnancy and breastfeeding.
[https://www.frontiersin.org/journals/pharmacology/articles/10.3389/fphar.2020.594852/full]
Berberine is a Versatile Plant Compound that Helps to:
* support blood sugar balance,
* improve metabolic efficiency,
* strengthen gut and liver function,
* reduce chronic inflammation and oxidative stress.
If you seek natural and science-backed support for your metabolism, berberine could be a valuable addition to your health routine.






FRESH 2024. THE HONEY OF THE YEAR IS NOW AVAILABLE!
2025 honey is now available!
FREE mõts with your order!
New customers favorites – here are the 6 products customers loved the most!
Propolis bundles -
discounted price!
By purchasing 2 balms, you will get lip balm as a gift!
Stimulate skin renewal processes!